The integration of artificial intelligence into telehealth has transformed the healthcare landscape, offering innovative solutions and promising a future where healthcare is more accessible, efficient, and patient-centered.
AI’s current role in telehealth is multifaceted, enhancing patient care through improved diagnostic accuracy, personalized treatment plans, and better patient monitoring. Additionally, AI tools and platforms reduce the workload on healthcare professionals and allow them to focus more on patient care management. AI’s potential in the future is expected to allow real-time tracking of patient vitals and alert healthcare providers to potential health issues before they become critical.
Introduction
AI in healthcare is no longer something on the horizon—it has already become a cornerstone in improving patient care, streamlining operations, and enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
Scheduling and attending a medical appointment at the tap of the finger is convenient and low-effort for anyone with a busy schedule, but particularly beneficial for patients with mobility issues or those from rural or underserved areas.
Statistics show that the benefits go both ways as around 75% of healthcare organizations that have integrated AI into their operations have seen enhancements in their ability to treat diseases effectively. Furthermore, 80% of these facilities observed that using AI technology has helped reduce staff burnout.
Why The Need for AI in Telehealth
The number of chronic diseases and particularly the prevalence of these diseases in young people and adolescents, has increased over the last years. In the US alone, chronic illnesses, like heart disease, cancer, respiratory disorders, and diabetes, account for nearly 75% of deaths worldwide each year. Many of these early deaths are preventable, with preventive care and lifestyle medicine playing a central role in reducing this burden.
Moreover, preventative care and longevity are now key areas of focus in medical research.
Today, preventative care can be seamlessly integrated with artificial intelligence tools. The days of relying solely on physical examinations for diagnoses are evolving. In fact, research shows that physical exams accounted for only 11% of the diagnostic process, while the patient’s history made up 76%.
Both patients and doctors can now use a mix of objective data and expert analysis to reach conclusions. In recent years, AI has become a valuable tool in helping medical professionals assess and interpret this data more efficiently. AI algorithms can rapidly process large datasets, allowing medical professionals to identify potential health risks early – often before they are detectable by traditional methods.
This is particularly important in fields like oncology, where cancer risk profiles can vary based on disease progression patterns. AI can enhance predictions by simulating how diseases develop and change over time.
An increasing number of hospitals are leveraging AI tools to optimize the use of their resources.
Notable AI Telehealth Companies and Their Achievements
Beyond faster data analysis, AI has recently driven several breakthrough innovations in healthcare, including:
- Allowing mammograms to be analyzed at 30 times the speed with nearly perfect accuracy, significantly decreasing the necessity for biopsies
- Making important steps in expanding the technology to lower lung cancer death rates globally (something that AstraZeneca has decided to pursue)
- Enhancing CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) technology – a powerful tool for editing genomes, allowing researchers to alter DNA sequences and modify gene function.
Other examples include:
- Cerebral – delivers top-tier mental health services, integrating therapy and medication management for well-rounded care.
- Doctor on Demand – a platform that delivers 24/7 online medical services for urgent care, mental health, and therapy, offering round-the-clock access to healthcare professionals.
- BetterHelp – a digital therapy service that links users with licensed therapists via video, messaging, chat, and phone calls. Prioritizing accessibility and convenience, it provides therapy options for individuals, couples, and children.
- MDLIVE – offers virtual healthcare services for both medical and mental health needs. With on-demand access to board-certified physicians and licensed therapists, their goal is to deliver quick and convenient healthcare solutions.
AI Advancements in the Wellness Sector
AI tools have made significant strides in the wellness sector, with wellness apps emerging as a rapidly growing part of the broader AI industry.
Their growing popularity is driven by advanced features like personalized recommendations, real-time tracking, and predictive analysis.
AI-powered wellness and fitness apps can assess users’ eating habits and nutritional requirements, delivering customized meal plans. This allows users to meet their health goals more effectively through tailored dietary guidance.
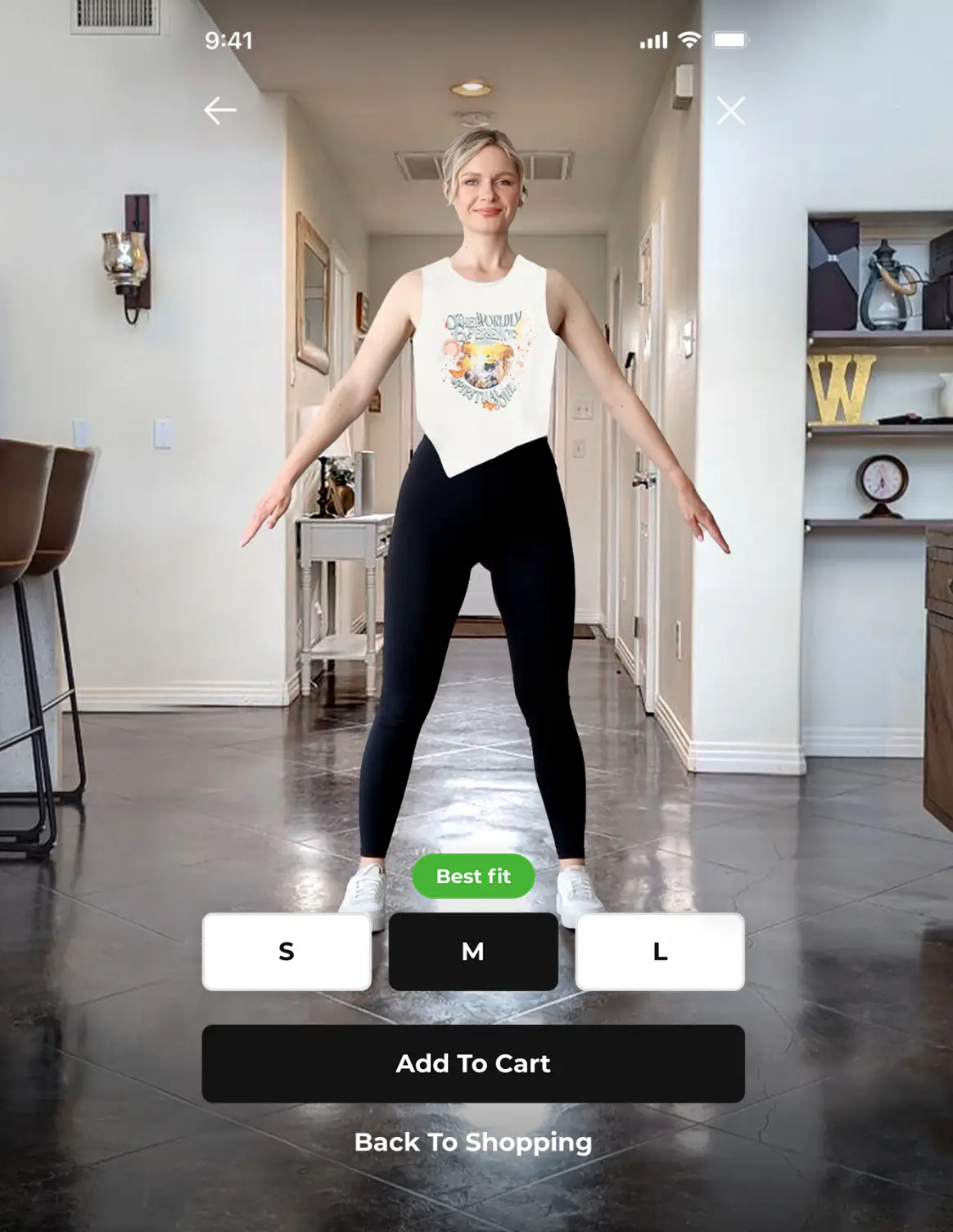
One example is FitXpress, which delivers the necessary body data to create personalized health insights and lifestyle suggestions, helping users make lasting improvements for sustainable weight loss and better long-term health outcomes.
FitXpress generates a detailed 3D model and provides over 80 precise body measurements, along with key body composition metrics such as BMI, BMR, and body fat percentage—all from just two smartphone photos.
This information allows users to better understand their current physical condition and track changes over time. Users can regularly scan their bodies to monitor progress, with the 3D models offering a visual representation of body changes, providing added motivation. The platform provides AI-driven data so that businesses can create exercise programs tailored to fitness levels and goals, helping optimize fat loss and improve overall health.
With the rise of wearable devices, AI enables monitoring of health indicators like heart rate, sleep, and activity levels. These devices assess data, predict potential issues, and allow for early intervention to improve fitness and health outcomes.
The Rise of AI in Telemedicine
With a strong reliance on AI technology, the telemedicine industry was estimated to be worth around 79.93 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow to $290.90 billion by 2032.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, over 97% of healthcare professionals adopted telemedicine in their practices, reflecting the growing integration of digital health technologies, many of which are powered by AI. Healthcare providers utilizing AI have improved patient care, with AI enabling more precise diagnoses and creating tailored treatment plans.
One notable example was the implementation of AI-driven diagnostic tools, which played a key role in analyzing medical images like chest X-rays and CT scans to identify indications of COVID-19 pneumonia. The speed at which these tools operated was essential in handling the large influx of patients, enabling prompt medical intervention.
Moreover, companies such as Infervision and Qure.ai created AI algorithms that were integrated into hospital systems to support radiologists in more accurately and rapidly detecting COVID-19 cases. These AI solutions were capable of processing images in mere seconds, offering vital assistance in healthcare environments under strain.
Telemedicine has simplified data collection and transmission, making it easier to perform remote assessments. However, the reliance on expensive imaging technologies and high-end examinations has raised costs without necessarily improving the quality of care.
Taking a patient’s history could be a cost-effective and valuable part of telehealth, but it’s often underused due to its time-consuming nature. AI has the potential to improve this by offering suggestions, diagnostic clues, and follow-up questions based on patient responses, making the process more efficient and thorough.

This efficiency extends to virtual triage, where AI tools gather basic details like demographic information and risk factors, followed by symptom-specific questions. It accommodates a wide age range, from newborns to adults.
Based on the initial input, the AI system generates a series of questions that mirror the diagnostic methods doctors would use. These questions focus on key factors like symptom severity, duration, aggravating conditions, and related symptoms. Typically, after answering 10 to 20 questions, the AI reaches a level of confidence sufficient to provide a reliable triage recommendation.
The system then generates a results page that outlines the suggested next steps, which could range from self-care advice to recommending a consultation with a healthcare professional or directing the patient to urgent or emergency care. The recommendations also include advice on the most appropriate consultation method, whether in-person or remote.
Today’s Use Cases of Artificial Intelligence in Telehealth
Remote Patient Monitoring and Management
AI has significantly advanced remote patient monitoring (RPM), enabling continuous monitoring of patients’ health conditions without the need for frequent hospital visits. AI-powered devices and sensors can collect data on vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels, and transmit this data to healthcare providers in real time. Machine learning algorithms analyze this data to detect anomalies and predict potential health issues before they become critical.
Example: The KardiaMobile app, developed by AliveCor, is a portable ECG device that allows patients to record their heart’s electrical activity anywhere, anytime. The AI in the app analyzes the ECG readings to detect arrhythmias such as atrial fibrillation and alerts both the patient and their healthcare provider if an abnormality is detected.
Virtual Health Assistants and Chatbots
Virtual health assistants and chatbots are among the most common applications of AI in telehealth. These AI-driven tools provide instant, personalized interactions with patients, offering advice, answering questions, and even scheduling appointments. They help alleviate the workload of healthcare providers by handling routine queries and administrative tasks.
Example: Ada Health is an AI-powered chatbot that conducts symptom assessments by asking patients a series of questions about their symptoms. Based on the inputs, Ada provides possible causes and recommends next steps, such as seeing a doctor or visiting an emergency room. This tool helps patients make informed decisions about their health while reducing unnecessary visits to healthcare facilities.
This isn’t just an eBook – it’s your roadmap to the future of health and wellness. Packed with actionable insights and fascinating stats, it’s essential reading for anyone in the fitness, health, or telehealth industries.
AI-Assisted Diagnostics
AI is playing a crucial role in improving diagnostic accuracy and speed, especially in radiology and pathology. AI algorithms can analyze medical images such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to identify abnormalities faster and more accurately than human radiologists in some cases. This capability is particularly valuable in telehealth, where remote diagnosis is often necessary.
Example: Viz.ai is an app that uses AI to detect signs of a stroke in CT scans. The software analyzes the images and alerts the healthcare team if it identifies a potential stroke, allowing for quicker intervention and treatment. This reduces the time to treatment, which is critical in stroke care, potentially saving lives and reducing long-term disability.
Early Detection of Health Issues
With wearable devices and sensors continuously collecting patient data, AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of information to detect concerning changes. When abnormalities are identified, the system promptly alerts healthcare providers, allowing for early intervention and the prevention of more serious health issues.
This leads to better patient outcomes and helps cut healthcare costs by streamlining routine tasks and enhancing overall efficiency. For instance, AI can optimize staff schedules and improve patient management, reducing both wait times and the length of hospital stays.
Personalized Medicine and Treatment Plans
AI is enabling personalized medicine by analyzing large datasets to understand the unique characteristics of individual patients. In telehealth, this capability allows for the creation of personalized treatment plans based on a patient’s genetic makeup, lifestyle, and other factors. AI can also predict how patients will respond to specific treatments, allowing for more tailored and effective care.
Example: Merative offers AI-driven insights to help healthcare providers deliver personalized care. Its AI algorithms analyze a vast range of data, including medical literature, clinical trial data, and patient health records, to recommend tailored treatment options for individual patients. This can be particularly beneficial in complex cases, such as cancer treatment, where personalized care is crucial for better outcomes.

Behavioral Health and Mental Health Support
Telehealth has expanded access to mental health services, and AI is enhancing these services by providing tools for early detection, intervention, and continuous support.
The key advantage lies not only in personalization but also in adaptability. As the AI gathers more data about the user, it continually updates its recommendations, evolving in real-time to respond to changes in the body. This is something that FitXpress can deliver perfectly. The app can track and analyze eating patterns and physical activity, to provide insights into an individual’s overall health and suggest lifestyle changes to support weight loss.
This approach simplifies the process by automating planning, decision-making, and progress tracking, making weight loss easier and more attainable for individuals.
Moreover, AI-powered apps can monitor patients’ mental health through regular check-ins and assessments, and even detect changes in behavior that may indicate a mental health crisis.
Example: Woebot is an AI-driven chatbot designed to provide mental health support. The app uses NLP to engage users in conversations about their mental health, offering cognitive-behavioral therapy techniques and mindfulness exercises. Woebot can track users’ moods over time and provide tailored recommendations, offering a valuable tool for ongoing mental health support.
Streamlining Administrative Tasks
AI is also improving telehealth by automating administrative tasks such as billing, coding, and scheduling. This not only reduces the burden on healthcare providers but also minimizes errors and improves efficiency. AI can process claims faster, predict patient no-shows, and optimize appointment scheduling, leading to a more efficient telehealth service.
Example: Augmedix provides ambient medical documentation and data solutions. The platform uses generative AI, including proprietary natural language processing (NLP) and large language models (LLMs), to create medical documentation.
Clinicians can control the creation of medical notes through an intuitive interface, offering features like summaries of key medical events. Additionally, Augmedix’s solutions are integrated with leading electronic health record (EHR) systems, enhancing operational efficiency without disrupting existing workflows.
AI in Telehealth Has Its Challenges
Bias in AI models – biases can stem from the data used to train the AI systems, which may not be representative of the diverse patient populations. Such biases could lead to inaccurate or discriminatory medical recommendations. The solution would be to employ techniques that reduce bias and ensure AI models undergo rigorous fairness evaluations.
Data privacy and security – the vast amounts of data required to train AI models raise significant data privacy and security concerns. With the reliance on third-party software for computational resources, there’s a risk of exposing sensitive patient information. Institutions may consider local hosting of AI models to alleviate some of these concerns.
Regulatory and ethical considerations – the implementation of AI in telehealth must navigate complex regulatory landscapes. Ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations and addressing ethical considerations, such as the extent of AI’s decision-making role, are vital for the successful adoption of AI in telehealth.
Technological challenges – the lack of technological experience among healthcare staff is a notable barrier. There’s a pressing need for digital training to equip frontline healthcare providers with the necessary skills to utilize AI tools effectively.
The Future of AI Tools and How They Will Impact the Telehealth Industry
Gene Therapy to Combat Genetic Disorders
AI already plays a key role in advancing gene therapy by analyzing genomic information to detect genetic mutations linked to diseases. In the future, AI will further enhance the development of personalized gene therapies and help predict their effectiveness in patients.
Combining various data sources, AI enhances the accuracy of predicting both the efficacy and safety of gene therapies. It builds models that forecast treatment results and refine therapy protocols, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Through its ability to analyze genomic and molecular data, AI will identify critical patterns and potential biomarkers. This process will support the discovery of new therapeutic targets, improve patient classification strategies, and help establish markers for monitoring the success of treatments.
Improved Drug Discovery
AI significantly expedites the drug discovery process by analyzing genetic data to pinpoint potential drug targets and predict how genetic variations may impact a drug’s effectiveness. This approach will help develop more precise and effective therapies.
Researchers are also developing AI models capable of quickly diagnosing cancer and predicting treatment outcomes by analyzing pathology images alongside genomic and clinical data.
Additionally, scientists aim to explore mechanisms related to Alzheimer’s disease progression. This research will enhance the ability to predict individual responses to therapeutic interventions for the disease.

Enhanced Diagnostic Capabilities
One of the most promising trends in AI for telehealth is the continued advancement of diagnostic tools. AI-powered algorithms are becoming increasingly sophisticated at analyzing medical data, including imaging scans, lab results, and even patient histories. These tools are expected to improve the accuracy and speed of diagnoses, enabling healthcare providers to identify conditions earlier and more reliably.
For example, AI-driven diagnostic tools that analyze medical images, such as those used in radiology, will become more prevalent. These diagnostics tools can detect subtle patterns that may be missed by human eyes, offering an additional layer of scrutiny. As AI continues to learn and evolve, it is likely to surpass human diagnostic capabilities in certain areas, leading to more accurate and timely diagnosis, which is crucial in managing diseases and improving patient outcomes.
For example, Aidoc and other health tech companies use AI to analyze medical images for conditions like fractures, brain hemorrhages, and lung diseases with remarkable speed and accuracy.
Companies like SkinVision are using AI to assess skin cancer risk, allowing for early detection and timely intervention. As AI technology continues to advance, we can expect even more accurate and comprehensive diagnostic capabilities in telehealth services.
Highly Personalized Medicine and Treatment Plans
The future of telehealth will also see AI playing a critical role in the development of personalized medicine. AI systems will analyze vast amounts of data, including genetic information, lifestyle factors, and patient history, to create highly individualized treatment plans. These plans will be tailored to the specific needs of each patient, taking into account their unique characteristics and medical history.
AI-driven personalized medicine will allow healthcare providers to predict how a patient might respond to certain treatments, helping to avoid ineffective therapies and reducing the likelihood of adverse reactions. This trend will make telehealth a more precise and patient-centered approach to healthcare, ultimately leading to better health outcomes and increased patient satisfaction.
Human-Like Virtual Health Assistants
Another trend to watch is the development of AI-assisted virtual health assistants. These AI-driven tools will provide patients with 24/7 access to healthcare information and support, helping them manage their health more effectively.
Virtual health assistants will go beyond answering medical questions, offering reminders for medication, and scheduling appointments. They will add mental health support to their list of capabilities and become more advanced, understanding natural language and responding in a way that feels like talking with a real human person. Over time, they will be able to act as the first point of contact for patients seeking medical help. This will reduce the burden on healthcare providers, allowing them to focus on more complex cases while still ensuring that patients receive proper care and the information they need.
Patient Monitoring Combined with Predictive Analytics
Remote monitoring is another area where AI is expected to make significant strides. Telehealth already allows patients to receive care from the comfort of their homes, and AI will enhance this capability by enabling more effective remote monitoring of chronic conditions and post-operative care.
AI algorithms will analyze data from wearable devices, such as heart rate monitors, glucose meters, and blood pressure cuffs, to detect early signs of complications or disease progression. Predictive analytics will allow healthcare providers to intervene before a condition worsens, potentially preventing hospitalizations and improving overall patient outcomes.
Furthermore, AI will help identify trends and patterns in patient data that may not be immediately apparent to human clinicians. This will enable more proactive and preventive care, shifting the focus from reactive treatment to preventive and ongoing health management.
For example, a patient with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) might use a smart inhaler that tracks usage patterns and measures lung function. AI can analyze this data to detect worsening symptoms and alert the patient or their healthcare provider to adjust treatment accordingly. Companies like Propeller Health are already using this technology to help patients manage respiratory conditions more effectively.
Final Thoughts
The integration of AI in the telehealth and telemedicine market is a game-changer, enhancing the delivery of healthcare services through improved diagnostics, personalized care, and streamlined operations. From AI-driven remote patient monitoring to virtual health assistants and mental health support, AI applications are making healthcare more accessible, efficient, and effective.
Yet, AI tools don’t provide diagnoses or make final healthcare decisions for patients. Instead, they function as educational resources, helping patients gain the knowledge needed to make informed choices about their treatment options. Additionally, AI-enabled telehealth helps doctors in providing effective and efficient care.
With careful planning and collaboration, AI can become the baseline of modern healthcare, offering unprecedented levels of care and support to patients around the world.