Consumers’ increased awareness about the fashion industry’s environmental and social impact calls for sustainable solutions. Largely dictated by consumer demand, the fashion industry continues its journey toward eco-friendly and ethical clothing manufacturing and production.
From pollution and resource depletion to labor exploitation, traditional apparel production processes have been under fire for their unsustainable and sometimes unethical practices. Amid growing awareness and demand for ethically produced garments, the fashion industry is transforming. Today, sustainable clothing production techniques emerge as a beacon of hope, offering a path to a more eco-friendly, less wasteful, and socially responsible future.
“Fashion can be incredibly wasteful and damaging to the environment, but it doesn’t have to be.”
Stella McCartney

The stark truth is that the fashion industry is massive and progressively expanding, but it’s also the sixth most polluting industry in the world.
Statista forecasts that the global apparel market will surge in worth, escalating from $1.5 trillion in 2020 to a staggering $2.25 trillion by 2025. While this exponential growth offers significant economic opportunities, it raises concerns about its potential ramifications.
These include heightened environmental impacts, amplified challenges in managing global supply chains, exacerbated efficiency issues for fashion brands and retailers, and increased consumption rates worldwide.
On the bright side, sustainability practices have started to gain more traction. Thus, more companies are reorienting the industry and consumers away from the fast fashion model and toward sustainable sourcing, production, and distribution.
Moreover, digital solutions gradually foster greater eco-responsibility, diversity, and inclusivity within the industry. If all fashion brands embrace these solutions wholeheartedly, the industry will address fashion’s sustainability challenges through evolving initiatives, like reselling, sustainable sourcing of raw materials, and customization of fashion through on-demand manufacturing solutions.
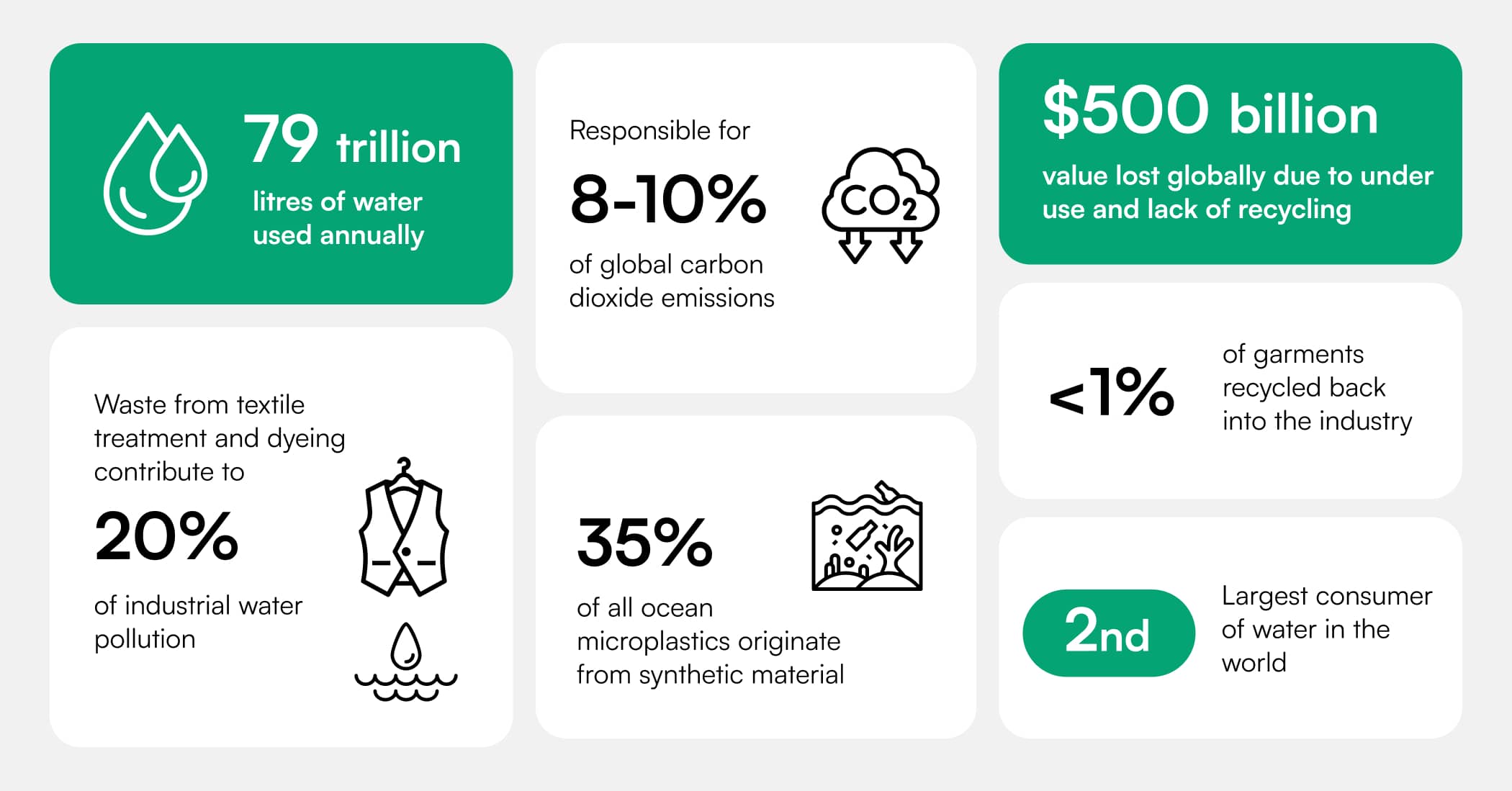
The Rise of Sustainability in the Fashion Industry
With growing awareness of environmental and social issues, consumers have increasingly demanded ethically produced and eco-friendly clothing.
As a McKinsey survey highlights, 67% of consumers consider sustainable materials an important purchasing factor, and 63% view a brand’s promotion of sustainability similarly.
The fashion brands that have evolved manufacturing processes and embraced sustainability as a core value have also enjoyed economic success.
According to a Statista report, the sales share of sustainable clothing has steadily risen over the past decade, and the trend is forecasted to continue, with the market share set to reach over 6% by 2026.
The younger generations drive this growth, with millennials and Gen Z accounting for an estimated 68% of sustainable apparel revenue in the United States in 2022.
Environmental issues aside, ethical considerations about labor practices have also come to the forefront. Reports of exploitative labor and sweatshop conditions in garment factories have ignited consumer outrage. In countries like the Philippines or Bangladesh, children are still used as laborers in the garment industry.
As a result, consumers are increasingly drawn to brands that ensure fair wages, safe working conditions, and ethical treatment of workers throughout the manufacturing process.
Additionally, transparency and traceability have become key buzzwords in the sustainable fashion movement. Consumers want to know where their clothes come from, how they’re made, and under what conditions. Genuinely sustainable fashion brands should offer transparency in their supply chain, from sourcing raw materials to manufacturing and distribution.
In this regard, the global fashion industry needs to make faster progress. According to the 2023 Fashion Transparency Index, only half of the major fashion brands revealed their supplier list.
A positive example is Patagonia, known for its outdoor apparel. Patagonia is a pioneer in ethical fashion as the company has implemented fair labor practices, supports fair trade, and regularly audits its supply chain to ensure compliance with labor standards. Moreover, the brand is renowned for its commitment to sustainability across its product lines, which has garnered a loyal following among environmentally conscious consumers.

Key Players Leading the Way in Sustainable Fashion
While some brands have supported and promoted sustainability from the get-go, others have later adjusted their efforts to become environmentally friendly and promote social responsibility in the fashion industry.
Several sustainable clothing manufacturers have emerged as leaders in the fashion industry, combining style with eco-conscious practices.
The examples include:
- Eileen Fisher – a brand that focuses on timeless designs and sustainable materials, like organic cotton, recycled fibers, and responsible production processes. Eileen Fisher also operates recycling and resale programs to extend the lifespan of its garments.
- Reformation – a company known for its chic and trendy clothing made from sustainable materials. Reformation prioritizes eco-friendly fabrics like Tencel, organic cotton, and recycled polyester. The brand also implements energy-efficient manufacturing practices and offers carbon-neutral shipping.
- Veja – this French footwear brand prioritizes ethical sourcing and sustainable materials. The brand’s sneakers are made from organic cotton, wild rubber from the Amazon rainforest, and recycled plastic bottles.
- Pact – specializes in affordable and eco-friendly basics, including clothing and underwear. The brand uses organic cotton and fair trade practices to create comfortable and sustainable garments. Pact is committed to transparency and regularly audits its supply chain to ensure ethical production standards.

Exploring Sustainable Clothing Production Techniques
Sustainable clothing production begins with the selection of materials. Traditionally, the fashion industry has relied heavily on resource-intensive materials like conventional cotton and synthetic fibers derived from petrochemicals.
However, today’s sustainable brands are turning to innovative alternatives, like:
- Organic Cotton – grown without synthetic pesticides or fertilizers, organic cotton reduces chemical pollution and minimizes water consumption.
- Hemp – a versatile and eco-friendly crop, hemp requires minimal water and pesticides to grow, making it a sustainable alternative to conventional fibers.
- Recycled materials – from recycled polyester made from plastic bottles to regenerated nylon derived from discarded fishing nets, recycling technology is enabling the fashion industry to reduce its reliance on virgin materials and divert waste from landfills.
- Eco-chemical management – sustainable practices involve replacing toxic chemicals with safer alternatives and implementing strict chemical management systems to ensure that any chemicals used do not harm the environment.
Examples of brands committed to sustainable practices and the use of eco-friendly materials in their products include:
Eco-friendly textile manufacturers
- Ananas Anam Ltd –based in London, the textile company developed Pinatex, a natural leather alternative made from pineapple leaf fiber.
- Belrey Fibres – a textile recycling company based in Belgium that converts post-industrial filament waste into reusable fibers.

Organic clothing manufacturers
- Pact – known for affordable fair trade basics, they use GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard)-certified organic cotton in their products.
- Nature USA – a leader in sustainable fashion, offering eco-friendly apparel design and manufacturing services; the company uses circular fashion, zero waste production, and private label options for its clients.
3DLOOK aids various fashion manufacturers in refining their production processes through its Mobile Tailor solution. This system allows fashion companies to obtain precise body measurements via 3D body scanning, improving inventory management and reducing material waste. Streamlined production cycles from these accurate measurements enhance efficiency and lower energy use and carbon emissions, contributing to less overall waste and a better fit for custom clothing.
Technological Advances in Ethical Fashion Technology
From blockchain to AI, 3D printing to sustainable materials, technological innovations are paving the way for a future where fashion looks good and does good for the planet.
Biofabrication and sustainable materials
One of the most promising technological advancements in ethical fashion is the development of biofabrication. Companies like Bolt Threads and Modern Meadow are engineering sustainable materials using biotechnology.
Bolt Threads, for instance, has created Microsilk™, a protein-based material inspired by spider silk that offers a cruelty-free alternative to traditional silk production. Similarly, Modern Meadow produces biofabricated leather using a process that eliminates the need for animal hides, significantly reducing the environmental impact of leather production.
3D Printing and On-Demand Manufacturing
3D printing technology enables on-demand manufacturing and reduces waste by using organic, biodegradable, and recycled materials. This approach not only eliminates the need for excess inventory but also allows for greater design flexibility and personalization. Digital fabric printing has emerged as a method to offer unique patterns and designs while reducing dye and water usage.
Brands like Mango, Pangaia, and even footwear companies like New Balance and Adidas use 3D printing to produce customized garments and shoes with minimal material waste. This approach eliminates the need for excess inventory and allows for greater design flexibility and personalization.
Blockchain and supply chain transparency
Blockchain technology enhances transparency and traceability in the fashion supply chain. Companies like VeChain and Provenance are implementing blockchain solutions to provide a transparent and tamper-proof record-keeping system.
In essence, blockchain helps consumers trace the journey of their garments from raw materials to finished products, enhancing accountability and promoting ethical practices.
AI and sustainable fashion design
Artificial intelligence (AI) is most often used for design optimization and to help brands reduce waste by predicting trends and consumer behavior. Moreover, AI can streamline production processes, leading to more efficient use of resources and less environmental impact.
For instance, Intelistyle’s AI-powered styling platform helps consumers make more sustainable fashion choices by suggesting outfit combinations based on their existing wardrobe and personal style preferences.
3DLOOK’s Mobile Tailor solution uses AI-driven algorithms to accurately measure customers’ body dimensions. This ensures that customers select the right size the first time, reducing the likelihood of returns. It helps save resources and reduce waste associated with return shipping but also minimizes the environmental footprint of the fashion supply chain.
Further reading: Artificial Intelligence in Fashion: Reshaping the Entire IndustrySustainability Challenges and Solutions in the Fashion Industry

The fashion industry faces many challenges, from economic pressure to supply chain disruptions. However, innovative solutions are emerging to drive sustainable practices and reshape the future of fashion.
According to the latest McKinsey State of Fashion report, the fashion industry will likely face a global slowdown due to economic pressure. Rising costs of living and high inflation are causing consumers to tighten their budgets, a pressing issue that weighs heavily on brands.
Moreover, ever since the pandemic, the industry’s supply chain has known significant disruptions, making it difficult for suppliers to deliver what is expected and forecast future consumption patterns. Manufacturers are diversifying their operations into new territories to overcome geographical constraints and take advantage of reduced labor costs, access to raw materials, and proximity to consumer markets.
However, these workarounds are harshly criticized and viewed negatively by consumers, who are increasingly concerned about issues like inclusivity, fair pay, and working conditions.
Thus, fashion brands are expected to act and support the best interests of all parties and overcome environmental impact, distrust, and the lack of diversity.
Solutions to sustainable fashion are within reach

A growing number of sustainable clothing manufacturers are offering solutions tailored to the needs of small businesses, providing access to ethical production practices, eco-friendly materials, and transparent supply chains.
For example, Los Angeles-based manufacturer Kotn Studio partners with small businesses to produce ethically made garments using sustainable materials like organic cotton.
Regarding eco-friendly material sourcing, UK-based fabric supplier Offset Warehouse has offered small businesses access to a wide range of sustainable materials for their clothing lines. This way, the company helps small businesses reduce their environmental impact and appeal to consumers seeking sustainable fashion options.
Supporting small batch production, US-based manufacturer Lefty Production Co. helps small businesses with services like pattern making, sample development, and production management. Small brands can reduce waste, minimize inventory risk, and cater to niche markets with unique fashion offerings.
Although often criticized for its potential negative impact on the environment, Shein, fashion retailer, has been making efforts to address sustainability concerns. The company is implementing initiatives to minimize clothing waste, and sourcing more recycled materials.
Additionally, the company recently announced its intentions to extend its supply chain infrastructure and technology to other brands. An initiative labeled “supply chain as a service” would help brands experiment with new fashion items in smaller quantities and monitor their reception among consumers.
Case Studies: Success Stories of Sustainable Manufacturing Processes
Unspun.io is a sustainable fashion technology company pioneering on-demand manufacturing. Some of the ways they’re making a difference are through:
- Custom-Fit Denim Brand: Unspun has launched a custom-fit denim label based on a zero Inventory and minimized waste: the company follows a zero-inventory model via made-to-order clothing; this means they don’t hold stock and only create clothing pieces on demand, when these are ordered, significantly reducing textile waste.
- 3D Weaving: Unspun uses 3D weaving technology to reduce waste; instead of cutting and discarding extra fabric, the pioneering company has developed Vega™ technology, which transforms yarn into clothes in minutes. This allows for zero-waste production and circular reuse.
- Unspun has joined forces with Walmart to streamline clothing production, reduce waste, and enable on-demand, localized production, thus facilitating a low inventory model. This means Walmart can consolidate the supply chain necessary to make and distribute 3D woven work pants within the US, without affecting its competitive prices.
3DLOOK’s Mobile Tailor, is powering transformation to traditional apparel manufacturing. Where traditional manufacturing models often inaccurately predict consumer demand, leading to overproduction and inventory waste, an on-demand model powered by mobile body scanning drastically reduces these issues. It provides precise, individualized sizing, eliminating the need for customers to order multiple sizes for fitting, thus cutting down on returns and overcoming inconsistent sizing standards.
For instance, it helped Slø Jeans eliminate sizing inconsistencies by allowing customers to obtain accurate body measurements. Mobile Tailor’s integration with Slø Jeans’ online stores resulted in 90% accuracy, which solved the company’s issues with size-related returns and exchanges.

The Future of Sustainable Fashion Technology
The fusion of technology and eco-conscious practices is reshaping the fashion landscape, driving it to a more sustainable and ethical future.
One of the most significant trends in sustainable fashion technology is and will be the development of new materials that reduce environmental impact. Biotech textiles are leading the charge, offering alternatives to traditional fabrics that are both sustainable and biodegradable.
The concept of circularity is also gaining traction, with brands adopting a closed-loop system where materials are endlessly reused and repurposed.
The ethical dimension will become more crucial for building trust and loyalty among consumers who prioritize what they wear and the story behind it. Fashion transparency databases, industry certifications, and investigative reports will likely be far more accessible for consumers to reach and have at their disposal.
From the tech perspective, digital innovations will continue to be the linchpin in the quest for sustainable fashion. Integrating AI, biotechnology, and circular design principles will continue to evolve. Advancements in manufacturing automation and customization will make fashion more sustainable and more accessible and efficient for both brands and consumers.

Final Thoughts
The demand for sustainable fashion manufacturing is rising, driven by environmental consciousness, ethical considerations, transparency, technological innovations, and shifting consumer preferences.
The fashion industry’s path to sustainability presents numerous challenges but also opens vast opportunities for innovation and positive transformation. Technological advancements now enable all clothing manufacturers, not just the ethically focused ones, to meet growing demands for sustainability without sacrificing style or quality.
The best approach for brands is to align with customer expectations, embrace, and adopt more sustainable and ethical practices, thereby fostering a more responsible and sustainable fashion industry.