“Skinny, thin. Tiny, when? Everyone is talking about skinny jabs.”
The phrase “skinny jabs”, coined by UK tabloids, depicts the public frenzy concerning GLP-1 agonists Ozempic and Wegovy, which exploded in popularity after being used off label for weight loss, when celebrities using them and influencers sharing testimonials on social media.
These medical marvels lower diabetes treatment costs and transform into a cultural obsession. Scientists estimate over 500,000 people in Britain alone are using these “skinny jabs”, creating a $24 billion industry, estimated to reach $131 billion by 2028.
This explosion in popularity has created a compliance crisis. According to the investigation by Channel 4’s Dispatches program, pharmacies are issuing prescriptions too liberally. The study discovered pharmacies granting access to controlled drugs to people under the legal age limit and NHS nurses prescribing to people with average BMI—prompting a doctor to comment that the situation was “almost like the Wild West.”
UK Health Secretary Wes Streeting responded to these findings, calling them “deeply concerning” and emphasizing that “it is totally unacceptable for any retailer to prescribe them without the correct medical supervision and ID and age verification.”
Pharmacies can no longer rely on online forms and photos for verification to grant patients unrestricted access to these medications. As a response in 2025, the UK’s General Pharmaceutical Council added requirements for either in-person consultations, video consultations, or direct access to medical records from a GP. Compliance with these stipulations requires GP consent for access to medical files.
These changes in regulations are both challenges and solutions for healthcare providers, weight management clinics, and online pharmacies. The question is: how can providers achieve regulatory compliance and operational efficiency without creating friction in the patient journey?

The Verification Challenge: What Providers Are Facing
Unreliable Self-Reporting
Data reliability issues with weight reporting are the most challenging aspect for healthcare providers. Multiple UK healthcare providers estimate that 25-30% of cases involve incorrect weight input. Additionally, about 20% of failed orders occur because patients do not own scales, which renders them unable to accurately assess their weight. Patients manipulate reported measurements, and handling borderline BMI cases (weighing between a BMI of 28.5 and 31.5) is also a serious challenge.
Research from the National Library of Medicine indicates that women tend to underestimate their weight by an average of 2.35 kg while men do so by 1.41 kg, which is enough to make a patient ineligible for these medications.
A provider has pointed out, “The biggest challenge is deciding whether to prescribe medication for patients with BMI near the 30% cutoff, as small variations in weight can significantly impact eligibility.” Ethical dilemmas arise when patient expectations are set too high, balancing clinical appropriateness with patient expectations when data foundations are not trustworthy.
Inefficient Verification Processes
Managing weight verification prerequisites manually is inefficient, subjective and time-consuming. This includes verifying weight through full-body photographs which requires a back-and-forth between patients and healthcare professionals. Some providers report handling over 700 consultations weekly, making this verification unreasonable. Moreover, a fraction of patients wear loose-fitting clothing which can delay accurate BMI estimates.
An online pharmacy representative described it: “There is no standardized way to compare self-reported weight with submitted photos, leading to potential errors.” This gap increases variability within verification and puts the safety of patients and regulations aligned with the healthcare system at risk.
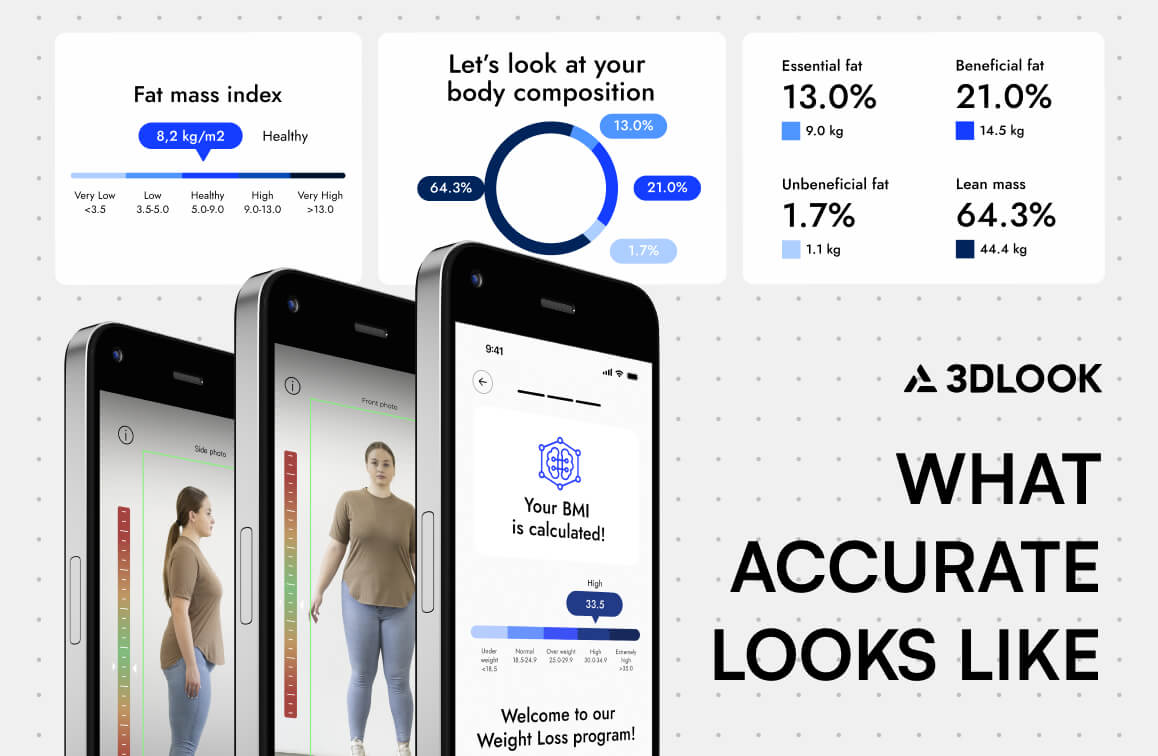
The Solution: AI-Powered 3D Body Verification
To tackle these compliance challenges, 3DLook’s FitXpress offers an AI-powered body scanning solution that authenticates weight and BMI measurements with no physical scales using only two photographs from a smartphone.
How It Works
Discrepancies between self-reported information and actual body measurements are tracked by FitXpress’s patented technology with an average accuracy of 3.5% (when users adhere to guidelines) within approximately 30 seconds. The process integrates into existing frameworks:
Guided Photo Capture: Users receive voice instructions to capture front and side pictures; automatic real-time pose validation ensures correct positioning. The system captures photos automatically when the correct pose is detected.
Accurate Processing: Height and weight inputs are compared with the AI prediction; all claimed inputs are verified. Only height input is required (weight supplied optionally), and the system achieves output in around 30 seconds.
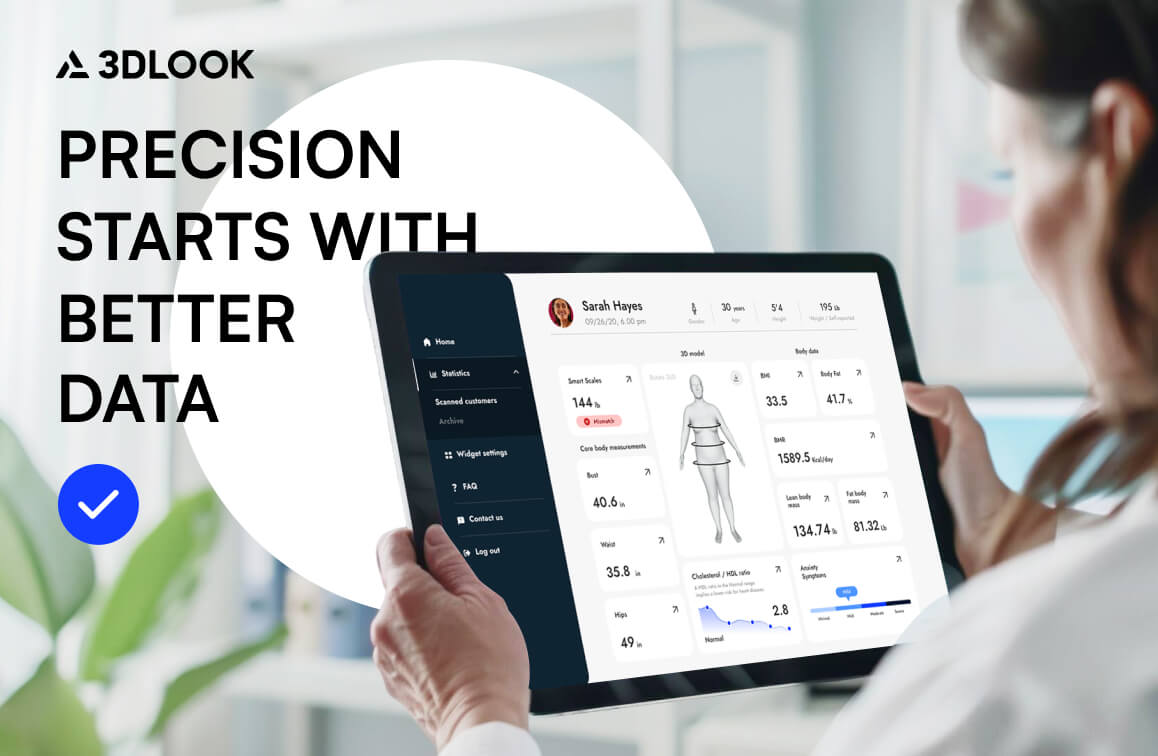
Comprehensive Results: The software creates patients’ 3D body models, provides dual BMI calculations, and discrepancy flagging for clinical review.
Benefits for Healthcare Providers
Enhanced Regulatory Compliance
AI-based body verification offers healthcare practitioners a reliable means of ensuring compliance. It meets new UK pharmacy regulations on independent weight verification and provides automated alerts for data discrepancies that could indicate fraud. The system allows flagging of borderline BMI cases for clinical scrutiny and establishes a documentable verification process.
As pharmaceutical regulatory expert Aleema Batchelor stated while being interviewed for Dispatches: “What we need is to make sure that those patients that are receiving these medicines do actually fall into the groups that most need them.”
This is beyond abiding by regulations; it demonstrates proper healthcare ethics. Clinical decisions need to rest on solid and objective data, especially for medications that affect up to 2% of patients.
Operational Efficiency
AI body verification yields important operational gains. The technology decreases the workload of manual verification for personnel, improving clinical workflows, and reducing time associated with verifying patient eligibility. The system offers scalability to providers who report 2000-3000 new subscribers each month while removing back-and-forth communications.
For practices with hundreds of consultations every week, this efficiency translates to savings, capability, and optimized costs, like having an additional employee whose only job is verification.
Improved Clinical Decision-Making
Modern AI body verification allows clinicians to view a patient’s entire body and provides complete body data. It enables personalized treatment by accessing over 80 precise body measurements which helps in better patient monitoring over time due to consistent methodology and visualization to educate patients about progress with weight changes. The system assists clinicians in detecting issues and actions before problems worsen.
The data allows healthcare providers to make precise decisions regarding medication approval and dosage, especially with patients who have borderline BMIs or atypical body shapes. As research in the International Journal of Obesity has shown, BMI data cannot be a robust proxy for determining health risks associated with obesity—additional body composition data is crucial for thorough patient evaluation.
Discover how AI-powered body data is revolutionizing health, fitness, and weight management, setting a new standard for personalization and progress tracking.
The Future of Weight Loss Treatment Verification
A focus on pharmaceutical therapies for obesity is expected to bring regulatory attention to the information structure used for approving such medications. The issues discussed in the latest round of probes will likely create more stringent verification processes, which may include independent verification of weight and BMI for all prescriptions of obesity medications with ongoing treatment supervision, standardized monitoring, verification standards for healthcare institutions, and diminished protection from administrative liability for inadequate fraud safeguards.
As the weight loss treatment market continues to grow, healthcare regulatory analysts estimate an accelerated formulation of regulations over the next five years, especially concerning remote consultations.
3D body verification and other technological solutions give providers the ability to satisfy existing requirements and address future regulations, enabling adjustment to patient care standards without compromising patient care.
Balancing Access with Safety
The new class of medications designed for weight loss offers a solution to obesity, which is a public health problem affecting almost two-thirds of adults in the UK. As one doctor highlighted during the Dispatches investigation, “They are a miracle drug, but I think the most important thing for doctors is that we first do no harm.”
Healthcare practitioners need to balance both sides of this issue. These drugs offer real promise for patients living with obesity and associated health problems, potentially changing lives by improving their mobility, alleviating joint pain, and reducing health complication risk factors.
At the same time, healthcare practitioners must accept ethical responsibility to guard against prescription management policies slackening. In the Dispatches investigation, the case of Mark Jones, a sheep farmer who was losing control of hypoglycemic episodes due to diabetes medication mismanagement, illustrates the clinical peril posed by supervision.
Final Thoughts
AI solutions for 3D body verification enhance operational and patient satisfaction. Technologies such as FitXpress enhance provider capabilities as it allows them to operate within regulatory frameworks, optimize business processes, obtain accurate clinical decision-making, and provide appropriate healthcare to patients with treatment needs.
Weight loss management is not “Wild West” as recent interventions suggest, but relies on systems that integrate sophisticated technology that ensure appropriate patients receive appropriate treatments, which advocates for all constituents within the healthcare system.